Super User
Hi-tech monitoring and carbon offsets for rainforests could be the big post-COP26 gain
A global carbon credits breakthrough at COP26 in Glasgow blew away any gloom from failing to phase out coal use, say many observers.
Discussion at the UN climate conference had been dominated by soaring atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, largely from fossil fuels but exacerbated by global deforestation, notably in tropical rainforests like the Amazon’s – often called the “Lungs of the Earth”.
But while COP26 failed to strike a coal deal, a carbon credit agreement could channel trillions of private sector dollars into protecting rainforests and farms, building renewable energy facilities and other projects to combat Climate Change and promote the circular economy needed to stabilise the Earth’s environment.
Nearly 200 countries at COP26 agreed to partially meet their climate targets by buying carbon credits/offsets created through the emission cuts of others.
This mechanism – originally put forward at the UN’s 2015 Paris Agreement - was previously held up by ‘double counting’: whether a credit could be claimed by both the country selling it and the nation buying it, but this was dropped, enabling the breakthrough.
 Hi-tech monitoring and carbon offsets for rainforests could be the big post-COP26 gain
Hi-tech monitoring and carbon offsets for rainforests could be the big post-COP26 gain
Brazil is now set to be a major beneficiary after decades of trying to balance national demand for farmland against international pressure to preserve the Amazon rainforest, which still dominates the country’s landscape, despite manmade shrinkage by nearly a quarter, from 4,100,000km² to 3,279,649km² over the past 50 years.
Writing in ‘Americas Quarterly’, former Brazilian Finance Minister and World Bank CFO, Joaquin Levy said: “Beyond helping Brazil protect the Amazon, a healthy global carbon market would create great opportunities for commercial and investment partners that could join the country in helping accelerate its journey to become a net zero economy before 2050.”
Former Brazilian ambassador and diplomat, Arnildo Schildt, led a COP26 delegation and agreed that the carbon credits deal gave a major boost to an international consortium he has steered for two years, negotiating with Brazil’s farmers and forestry associations, governments, the UN, international banks, academics, and industry partners as well as investors:
“We have been working to harness a ‘dynamic duo’ - highly advanced nano sensors and Digital Twin technology - to monitor density, height and emissions and protect the rainforest in real time whilst allowing building asset owners to trade carbon credits/offsets internationally and reward our farmers for their support.
“Carbon credit buyers then know that newly planted or established trees are not simply felled after the credits are bought. A secure market builds trust and certainty - massively important to credible buyers.”
Paul Stannard, Chairman of the not-for-profit World Nano Foundation applauded the initiative: “This would create a circular economy for rainforests and the farms around them, raising carbon credits of significant value to industries needing to offset emissions, while generating income for countries needing to alleviate pressure on rainforests.
“Two-thirds of the money will help sustain forests and eco-farms, with the remainder pledged to sustainable efforts in our major cities and urban spaces. Key projects will include renewable energy to help these countries drive down their own carbon emissions.”
Leading Digital Twin company Cityzenith – a World Economic Forum Global Innovator – has already developed its platform technology to incorporate carbon credits/offsets for the built environment and now aims to create a circular economy for the world’s buildings, farms, and forestry.
“This enhances the impact and savings, already estimated at a $280 billion, for the built environment alone,” said Cityzenith Founder and CEO Michael Jansen.
“We’re proud that Cityzenith is playing an ever-increasing role in tackling Climate Change and, with this initiative, advancing the circular economy cause.”
Lindsey Vest, Smart Cities & Smart Spaces Research Analyst for global technology intelligence firm ABI Research explained that a circular economy strategy would switch from mankind’s established but unsustainable ‘take-make-waste’ economy, adding:
“Circularity concepts such as remanufacturing, reuse, and the sharing economy will be critically enabled by smart cities technologies such as IoT (the Internet of Things – devices and systems that exchange data), AI and Digital Twins.”
ABI Research reported that many governments now plan to increase circularity, notably through the EU’s new Circular Economy Action Plan - part of its Green Deal - while China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) specifically targets Circular Economy Development.
This is in addition to work by organizations such as Cityzenith, Vodafone, the globally recognized Ellen MacArthur Foundation - dedicated to circular economy education and connection for companies and governments - and C40 Cities, whose 97 member cities generate 25% of global GDP and champion the circular economy
The World Nano Foundation is a not-for-profit membership organisation with 75,000 subscribers and users in 40 countries working on international commercialisation of nanoscale technologies in 16 industry sectors and collaborates with a wide variety of partners, maximising support and funding bringing advanced technology to the world and commerce. This is supported by many industries and academic groups developing and creating a legacy for enabling technology innovation.
Cityzenith is based in Chicago with offices in London and New Delhi. The company’s SmartWorldOS Digital Twin platform was created for anyone designing, constructing, and managing complex, large-scale building projects, properties, and real estate portfolios but has developed to cover infrastructure, energy projects, transport, health, people movements, and whole cities.
Kongsberg Digital (KDI) and Aker BP extends collaboration agreement to accelerate data utilization
The purpose of the agreement is to provide an enterprise-scale solution for real time data aggregation and visualization, helping Aker BP to improve performance, safety and optimize well operations.
Kongsberg Digital (KDI) is pleased to announce that it has signed a new extended contract with Aker BP to further strengthen the operator’s digital solutions. Building on an existing collaboration that has been ongoing since Aker BP was established, KDI will continue to contribute in accelerating Aker BP’s digitalization process by enabling real-time cloud-based data access, supporting decision-making, and improving efficiency.
“We are happy to further strengthen our collaboration with Aker BP through this extended agreement”, says Pedro Alcântara, SVP Digital Wells, Kongsberg Digital. “We appreciate that Aker BP continue to place their trust in the quality and performance that we offer with SiteCom”.

SiteCom- The industrial work surface for well operations by KDI
The SiteCom Enterprise Cloud is a centralized repository for real-time and historical data from drilling and well operations with an advanced platform where subscribers get access to powerful “plug and play” applications. The new agreement is delivered as a Software as a Service (SaaS), allowing Aker BP to scale according to operational requirements.
“It suits us to be the first company to take advantage of SiteCom Enterprise Cloud and the opportunities it enables. This will liberate more data and is another step in the digital transformation of our industry – a transformation where we not only intended to be first, but also best”, says Tommy Sigmundstad, SVP Drilling & Wells, Aker BP.
The contract was signed between Kongsberg Digital and Aker BP on 2nd November 2021, and the upgraded system integrations are expected to take place within the coming months.
SiteCom by Kongsberg Digital
Kongsberg Digital is a market leader in vendor neutral software solutions for oil & gas operators. The SiteCom Cloud has been built using the latest technology within cyber security and cloud technologies. With two decades of experience from utilization of real time data from drilling and well operations, SiteCom ensure robust and secure data transfer from client rigs to be accessed from any client location.
KONGSBERG DIGITAL
Kongsberg Digital, a subsidiary of KONGSBERG, is a provider of next-generation software and digital solutions, to customers within maritime, oil and gas, and renewables and utilities. The company consists of more than 500 software experts with leading competence within the internet of things, smart data, artificial intelligence, maritime simulation, automation and autonomous operations. Kongsberg Digital is the group-wide center of digital expertise for the KONGSBERG group.
KONGSBERG
KONGSBERG (OSE-ticker: KOG) is an international, leading global technology corporation delivering mission-critical systems and solutions with extreme performance for customers that operate under extremely challenging conditions. We work with nations, businesses and research environments to push the boundaries of technology development in industries such as space, offshore and energy, merchant marine, defence and aerospace, and more. KONGSBERG has about 11,000 employees located in more than 40 countries, creating a total revenue of NOK 25.6bn in 2020.
Follow us on: kongsberg.com
Aker BP
Aker BP is an independent E&P company with exploration, development and production activities on the Norwegian Continental Shelf. Aker BP is the operator of Alvheim, Ivar Aasen, Skarv, Valhall, Hod, Ula and Tambar. The company is also a partner in the Johan Sverdrup field. Aker BP is headquartered at Fornebu, Norway, and is listed on the Oslo Stock Exchange under the ticker 'AKRBP'. More about Aker BP at www.akerbp.com.
Metso Outotec introduces modular Horizontal Mill Plant Units for simple grinding circuit selection and execution
Metso Outotec is launching yet another unique solution in its range of minerals processing plant islands: the Horizontal Mill Plant Units. The pre-engineered plant units provide optimized grinding performance and simplify project management through easy circuit selection and flowsheet implementation. At the same time, they ensure safe operability and maintainability thanks to their state-of-the-art design. The plant units feature Metso Outotec’s industry-leading technologies including grinding mills, slurry pumps, hydrocyclones, conveying equipment, automation, and service support. The scope of the unit can be tailored according to project requirements (brownfield or greenfield, open or closed circuit).
“Choosing the right solution for a grinding process can be a complex task. In addition to financial and technological aspects, miners must also evaluate executional and operational factors. Our modular Horizontal Mill Plant Units have been developed to make it easier for customers to select and execute the best solution for their grinding needs. Our pre-engineered modules provide a safe and optimized solution for many grinding applications,” says Fernando Marques, Global Product Manager at Metso Outotec.
 Metso Outotec Horizontal Mill Plant Unit
Metso Outotec Horizontal Mill Plant Unit
The innovative Horizontal Mill Plant Units combine Metso Outotec horizontal mills, classification, pumping and automation technologies with a wide range of services and operation support. It takes sustainability and grinding performance to a new level by optimizing the usage of energy, water, grinding media and consumables.
Benefits:
- Grinding and classification expertise to support flowsheet implementation
- Pre-engineered modules for simple and rapid execution
- Process performance guarantee
- Easy process optimization thanks to comprehensive automation and digitalization features
- Sustainable technology with safe operability and maintainability
- Lifecycle service support
Read more about Metso Outotec Horizontal Mill Plant Units on our website.
Metso Outotec is a frontrunner in sustainable technologies, end-to-end solutions and services for the aggregates, minerals processing and metals refining industries globally. By improving our customers’ energy and water efficiency, increasing their productivity, and reducing environmental risks with our product and process expertise, we are the partner for positive change.
Metso Outotec is committed to limiting global warming to 1.5°C with Science Based Targets. We ranked 8th on the 2021 Global 100 list of the world’s most sustainable companies.
Headquartered in Helsinki, Finland, Metso Outotec employs over 15,000 people in more than 50 countries and its sales for 2020 were about EUR 3.9 billion. The company is listed on the Nasdaq Helsinki. mogroup.com
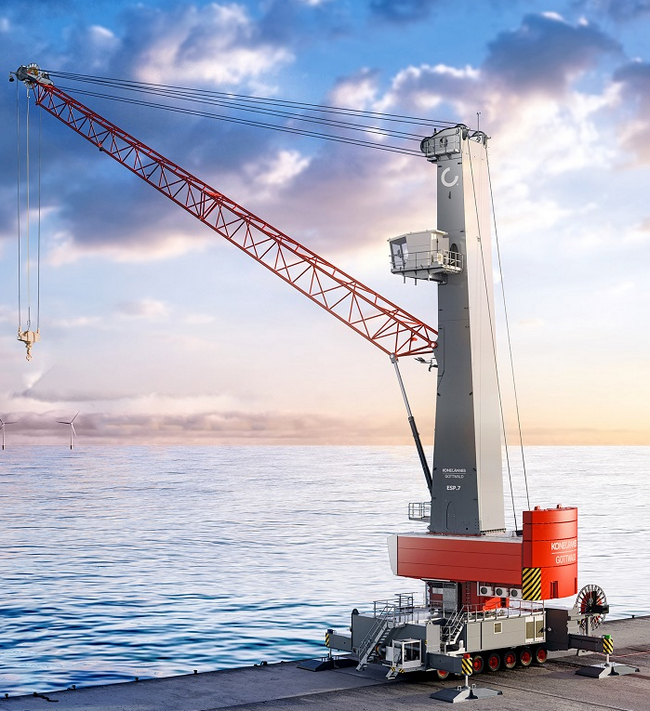
First Konecranes Gottwald Generation 6 Mobile Harbor Crane to Italy
Terminal San Giorgio S.r.l. (TSG) has ordered an eco-efficient Konecranes Gottwald ESP.8 Mobile Harbor Crane for its terminal in Genoa, Italy. Booked in November 2021, it is the very first Generation 6 crane to go to Italy. It will be delivered in June 2022.
Established in 2006, TSG has become the largest multipurpose terminal in Genoa, the busiest port in Italy. It is equipped to handle all kinds of freight including containers, breakbulk, project cargo, yachts, steel, and Ro-Ro.
Part of the Autosped/Gavio Group, a leading Italian logistics company, the terminal includes a number of intermodal rail and road connections to destinations around the country.
“We already operate two Generation 5 Konecranes Gottwald Mobile Harbor Cranes in Genoa, and they’ve always performed above and beyond our expectations, so we’re proud to be the first customer in Italy to order a new Generation 6. With its improved performance and additional features, we can’t wait to see how it handles containers and project cargo at our terminal,” says Maurizio Anselmo, Managing Director of TSG.
Innovative digital features and a fuel-optimized diesel generator set bring the crane in line with EU Stage V emission standards and Italy’s National Industry 4.0 Plan, a state strategy that encourages industrial innovation. The crane also has built-in readiness for an external power supply, so conversion to electric operation will be easy when resources allow. An additional service agreement will ensure that the cranes stay in good condition and provide TSG with maximum uptime.

“Our partnership with TSG is strong. With this new order, TSG will be able to experience the full potential of the Generation 6 crane in their operations. The order also shows the value of our sustained product development, as we continue to improve the productivity, reliability and fuel efficiency of our cranes,” says Gino Gherri, Regional Sales Manager for Konecranes Port Solutions.
The Generation 6 crane on order is a Konecranes Gottwald ESP.8 Mobile Harbor Crane, with a working radius of 54 m and a capacity of 150 t. A natural successor to the two Generation 5 cranes already on-site, it features stronger lifting capacity curves for improved performance and a higher classification for container handling, which doubles its service life in container handling operations.
A strong focus on customers and commitment to business growth and continuous improvement make Konecranes a lifting industry leader. This is underpinned by investments in digitalization and technology, plus our work to make material flows more efficient with solutions that decarbonize the economy and advance circularity and safety.
Konecranes is a world-leading group of Lifting Businesses™, serving a broad range of customers, including manufacturing and process industries, shipyards, ports and terminals. Konecranes provides productivity enhancing lifting solutions as well as services for lifting equipment of all makes. In 2020, Group sales totaled EUR 3.2 billion. The Group has around 16,500 employees in 50 countries. Konecranes shares are listed on the Nasdaq Helsinki (symbol: KCR).
New Alfa Laval CM Connect leverages digitalization to optimize hygienic processing
The new Alfa Laval CM Connect marks the next step in the digitalization journey to drive innovation and growth for customers in the hygienic processing industries. The CM Connect is a subscription-based condition monitor and cloud gateway. It enables plant operators to access data of rotating equipment on processing lines from a remote location. With data on actual runtime, trend analysis, and time to next service close at hand, plant operators can make informed maintenance decisions using their personal computers and mobile devices. This protects process continuity and critical assets, improves workplace safety, saves time and money, and delivers competitive advantage.
Maximize plant efficiency, minimize unplanned downtime
As Industry 4.0 evolves, the CM Connect is a natural next step on the customer digitalization journey, expanding the Alfa Laval range of condition monitoring solutions. With complete visibility of all connected assets, plant operators can detect issues that impact future performance, prevent unplanned downtime, and improve asset management.
Acting as a gateway communicating via Bluetooth, the CM Connect can link up to 10 Alfa Laval CM wireless vibration monitors launched last year. It then transmits the data over a 4G cellular network to the cloud for review and analysis on an intuitive, user-friendly dashboard.

Advanced real-time notifications
Advanced vibration analysis enables detection of any deviation from pre-set equipment threshold values. Should deviations occur, an SMS or e-mail notifies users who can take action in real time based on data analysis.
“Focus on what matters. The CM Connect lets plant operators plan and prioritize maintenance based on actionable data,” says John Walker, Portfolio Manager, Pumps, Alfa Laval. “Rather than replacing wear parts in advance of their useful service life, operators can spend time and money when and where maintenance is required.”
Besides linking the CM wireless vibration monitors, the CM Connect can also act as a sensor. It measures vibration, inboard temperature, and total runtime when mounted on Alfa Laval LKH, SRU, SX and DuraCirc pumps, or other rotating machines, such as agitators or mixers.
Towards enhanced digitalization
As part of the company’s commitment to pioneering digital transformation in the hygienic industries, Alfa Laval explores and develops Industry 4.0 solutions to advance competitive advantage for customers.
Learn more at www.alfalaval.com/cmconnect.
This is Alfa Laval
Alfa Laval is active in the areas of Energy, Marine, and Food & Water, offering its expertise, products, and service to a wide range of industries in some 100 countries. The company is committed to optimizing processes, creating responsible growth, and driving progress – always going the extra mile to support customers in achieving their business goals and sustainability targets.
Alfa Laval’s innovative technologies are dedicated to purifying, refining, and reusing materials, promoting more responsible use of natural resources. They contribute to improved energy efficiency and heat recovery, better water treatment, and reduced emissions. Thereby, Alfa Laval is not only accelerating success for its customers, but also for people and the planet. Making the world better, every day. It’s all about Advancing betterTM.
Alfa Laval has 16,700 employees. Annual sales in 2020 were SEK 41.5 billion (approx. EUR 4 billion). The company is listed on Nasdaq OMX.
Speaking a Common Language
Shared programming environment brings robot and CNC technologies together.
The last five decades have seen tremendous advances both in robotics and in CNC machining centre technology. In recent years manufacturers have begun reaping the benefits of bringing these two technologies together and robot tending of CNC machines is already helping to improve productivity for many businesses. However, there is more to come from these two important technologies thanks to the development of a single programming environment for both.
Barry Weller, Product Manager at Mitsubishi Electric, looks at the evolution of these two technologies, and the new possibilities for machine builders and OEMs to develop an important competitive advantage in the design of CNC machining centres, making it easy for their end users to reap the full benefits of automation.
A journey through the last 50 years of automation technologies is a story of increased sophistication and of democratisation. The products that were once state-of-art just a few decades ago would look like children’s toys today, while the high cost meant they were only available to a select few. The modern equivalents, while orders of magnitude more complex, are at the same time more compact, simple to use and readily affordable. Even on some of the biggest machinery assets where investment is still significant, the return on that investment can often be measured in months thanks to the increased productivity they deliver.
CNC machining and robotics are two good examples of this pattern. While CNC (computer numerical control) technology actually dates back to punch card programming of machines as early as the 1950s, CNC machines as we’d recognise them today – offering multi-axis, fully automated, computer-controlled milling and machining – are really quite a recent innovation. And with them has come a growing need for operators of this specialist equipment, with the Institute of Technical Trades US boldly claiming in 2016 that in many industries up to 40% of job positions would be in the field of CNC.
 With Mitsubishi Electric’s Direct Robot Control, a robot can be programmed using G-Code in the CNC machining centre itself.
With Mitsubishi Electric’s Direct Robot Control, a robot can be programmed using G-Code in the CNC machining centre itself.
Six decades of robot innovations
Robotics has seen a parallel evolution. The first industrial robots were developed in the late 1950s, with the Unimate in 1961 being the first commercially used industrial robot, lifting and stacking hot metal parts on a General Motors assembly line in New Jersey, USA. Another notable development came in in 1969, with Standford University presenting the first all-electric, 6-axis articulated robot – a combination of rotary, revolute, prismatic and spherical joints.
The 1970s brought the first robot arms as we’d recognise them today, with PUMA (Programmable Universal Machine for Assembly) arms which employed only revolute joints, increasing the dexterity of the arm. At the same time, elementary computing to control the position of the arm was introduced.
The 1980s saw a new take on robotics, with the University of Yamanashi in Japan pioneering a robot technology it called SCARA – selective compliance articulated robot. The arm had only four joints and was able to move in just X, Y and Z directions – hence the term ‘selective compliant’. But it had a number of advantages over more complex 6-axis arms, including speed, installation footprint and price. Mitsubishi Electric was one of the companies that commercialised the technology, and it quickly followed that development with the launch of a compact, 6-axis version that brought more dexterity to complex assembly processes.
Over the last 40 years Mitsubishi Electric has followed up those developments with the design of some 14 different generations of robot arms, each delivering improvements over the last. Some of the biggest advances have been in the reductions in robot cycle times; if we compare a robot model from 1998 to a modern-day equivalent, the contemporary version is six times faster. In contrast, in the same period, the speeds achievable by the fastest road cars have increased just 1.4 times, according to Auto Express.
It’s not just the baseline speed of the arm that has improved; modern arms will also accelerate faster, and they have more sophisticated control that gives them a smother motion. Both of these drive dramatic improvements in the cycle time of the application they are used in.
The number of models of robot that Mitsubishi Electric offers has also increased. Originally there were fewer than 10 to choose from; currently there are over 160 different variations with special modules and features tailored to the requirements of different industries. These include special coatings for the food and beverage sector, or special seals for clean room applications.
There have been significant developments in approaches to safety as well. Originally industrial robots operated behind fixed guards; today robots are designed with safety interfaces that allow them to operate without any fixed guarding, working even in close collaboration with people to bring new levels of flexibility to modern manufacturing processes.

Robot control technologies
Just as developments in computerisation brought increasingly sophisticated CNC machines, so advances in control systems have changed how robots can be used. Early robot designs relied on just digital signals to interface the robot with the rest of the machine’s control system. Now the robot and the machine’s Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) can be integrated onto the same platform, increasing the amount of data that can be transferred and the speed of the data transfer itself.
This availability of data has opened up new possibilities for improving productivity and getting the maximum return from the assets. Information on total run time and the performance of individual components within the robot can be used to provide predictive maintenance information, eliminating unnecessary machine stoppages and reducing unscheduled downtime. Data could also be passed up into the cloud where robots from different sites can be either managed or compared to see how they are performing.
Associated technologies have also evolved and progressed. It is now commonplace to have sensors on the end of the robot arms that can detect the force that is being applied, driving up quality. As an example, if the robot is inserting one part into another, then the force feedback to the control system can form a key part of the quality assurance process.
Vision sensors have also become commonplace in robot systems, enabling guidance of the robot to the required position. Importantly, their integration is now simple and practically seamless.
Perhaps the most important developments of all have come in the software used to program robots. These software tools vastly simplify the process of programming even the most complex of tasks while also allowing systems to be fully simulated before any hardware has been purchased, giving both engineering designers and their customers the peace of mind that a system will perform as planned.
Advances in software are at the heart of the most recent innovation: self-guided robots that use sensors to scan their environment and plan their motion path to avoid obstacles – all in real time. This means a further increase in the safety of robot installations, even where multiple robots and people are all working in the same space, enabling robots to operate without guarding.
Bringing robotics and CNC together
Recent years have seen CNC machine designers begin to embrace robotics, in particular for machine tending where robot loading and unloading of the machining centre can significantly increase overall throughput. This reduces the cycle time, but it also frees up human labour for more complex tasks, driving greater efficiencies and opening up new opportunities. For example, while machinists reconfigure the process for each new batch in short-run jobs, larger batch jobs can be configured to run overnight without requiring any changes.
For machine designers looking to integrate robotics into the CNC machining centre, and indeed for the customer’s operators who will need to work with the machine, there has traditionally been a stumbling block. The language used to program modern robotics is still very different to the G-Code programming language common on CNC machines.
For a skilled machine programmer or machinist, G-Codes enable a machining centre to be set-up relatively quickly. But this advantage is lost if they also have to learn a second language to program the robot, where the programming language is typically script-based. Now, though, Mitsubishi Electric has brought these two previously disparate fields of automation together with the new Direct Robot Control for its MELFA range of robots.
With this Direct Robot Control, rather than programming the robot and CNC separately, the robot can be programmed using G-Codes in the CNC machining centre itself. The robot is seen as another part of the machining job. Built into the MELDAS CNC controller – as used by a number of the largest CNC machine manufacturers – are a set of G-Codes that program and teach the robot. The robot can even be moved with the machine’s handwheel. All the alarms and warnings from robot and CNC are also recorded in the same log file.
This innovation opens up a whole realm of new possibilities in CNC machining, freeing companies from the need to find either two sets of specialist programmers or one who is adept in working with two different languages. It makes it easier for OEMs to integrate robotics into their CNC machine designs and provides a genuine competitive advantage for both them and their customers.
The last 50 years have seen massive changes and a rapid evolution in the fields of both robotics and CNC machining. The present has brought these two technologies together as never before, and doubtless there is more to come. A look at the benefits that tightly integrated robots have brought to other fields can yield some clues as to what the future might hold in the CNC world. Certainly, we can expect to see improved asset availability and perhaps the ability to bringing greater levels of automation even to high-mix, low-volume CNC machining. With technologies such as artificial intelligence also filtering through into mainstream automation components, we can expect machine learning in the robotised machining centre to also drive new efficiencies.
Perhaps we can’t confidently predict how machining processes will look in another 50 years’ time, but we can certainly anticipate that automation generally and the robotisation of CNC machines in particular – will play an increasingly important role.
About Mitsubishi Electric
With 100 years of experience in providing reliable, high-quality products, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (TOKYO: 6503) is a recognized world leader in the manufacture, marketing and sales of electrical and electronic equipment used in information processing and communications, space development and satellite communications, consumer electronics, industrial technology, energy, transportation and building equipment. Embracing the spirit of its corporate statement, Changes for the Better, and its environmental statement, Eco Changes, Mitsubishi Electric endeavors to be a global, leading green company, enriching society with technology. The company recorded consolidated group sales of 37.8 billion dollars* in the fiscal year that ended on March 31, 2021.
Mitsubishi Electric Europe, Industrial Automation – UK Branch is located in Hatfield, United Kingdom. It is a part of the European Factory Automation Business Group based in Ratingen, Germany which in turn is part of Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V., a wholly owned subsidiary of Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Japan.
The role of Industrial Automation – UK Branch is to manage sales, service and support across its network of local branches and distributors throughout the United Kingdom.
Supply Chain Alliance Supports Buzzard Phase II Achieve First Oil
Baker Hughes has been working alongside AGR Well Management, COSL Drilling Europe AS, Subsea 7 and Worley as part of a supply chain alliance to deliver CNOOC Petroleum Europe Limited’s (CPEL) Buzzard Phase II (BPII) development, which commenced production on Sunday November 21, 2021. Located about 100 kilometres (km) northeast of Aberdeen in approximately 96 metres of water, the CNOOC International-operated Buzzard platform is the largest UK North Sea oil discovery in the past two decades. BPII is a subsea development of the Buzzard northern area.
- Supply chain alliance includes Baker Hughes, AGR Well Management, COSL Drilling Europe AS, Subsea 7 and Worley
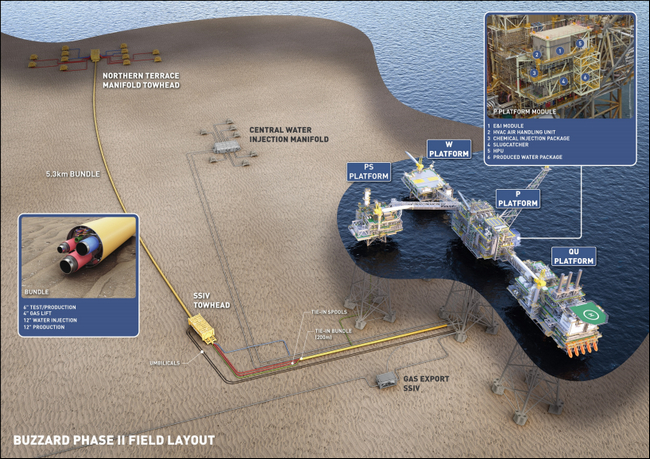
The BPII supply chain alliance was formed to offer an integrated and outcome-focused approach for the development. The partners, along with CPEL, have worked collaboratively to safely achieve first oil within the sanctioned budget and ahead of the revised schedule, which was significantly impacted by COVID-19.
This achievement is the result of a collective effort over a four-year period by the BPII supply chain alliance, as well as a long list of key suppliers and sub-contractors. More than 2.6 million hours were expended, working under an innovative contracting model which provided greater flexibility to quickly adapt to changes, including the global pandemic, and allowed teams to combine strengths.

“Baker Hughes has a long track record of successfully delivering complex projects, however we’ve also seen the challenges associated with projects of this scale,” Romain Chambault, vice president services and offshore, Europe and key accounts, Oilfield Equipment at Baker Hughes said. “Working collaboratively with the other companies in this alliance has helped to safely and successfully deliver the Buzzard Phase II development and created a model we hope to see replicated across other major energy projects.”
About Baker Hughes
Baker Hughes (NYSE: BKR) is an energy technology company that provides solutions for energy and industrial customers worldwide. Built on a century of experience and with operations in over 120 countries, our innovative technologies and services are taking energy forward – making it safer, cleaner and more efficient for people and the planet. Visit us at bakerhughes.com.
Seeq Corporation Achieves AWS Energy Competency Status
The designation recognizes Seeq’s expertise in enabling faster insights for energy customers via advanced analytics features and innovations.
Seeq Corporation, a leader in manufacturing and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) advanced analytics software, announced today that it has achieved Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) Energy Competency status. This designation recognizes that Seeq has demonstrated deep expertise helping customers leverage AWS cloud technology to transform complex systems and accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Achieving the AWS Energy Competency differentiates Seeq as an AWS Partner with extensive knowledge and technical proficiency within this unique industry, including proven customer success developing solutions across the value chain from production operations and optimization to commodities trading, new energy solutions, and more. To receive the designation, AWS Partners undergo a rigorous technical validation process, including a customer reference audit. The AWS Energy Competency provides energy customers with the ability to more easily select skilled Partners to help accelerate their digital transformations with confidence.
“Seeq is proud to be among the first AWS Partners to achieve the AWS Energy Competency status,” says Dr. Lisa Graham, CEO at Seeq. “Seeq and AWS are complementary solutions for the advancement of the energy industry. By choosing Seeq on AWS, energy companies can leverage the big data, machine learning, and computer science innovations they need to improve production and business outcomes.”
AWS is enabling scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions from startups to global enterprises. To support the seamless integration and deployment of these solutions, AWS established the AWS Competency Program to help customers identify AWS Partners with deep industry experience and expertise. To receive the designation, AWS Partners undergo a rigorous technical validation process, including a customer reference audit. Seeq also achieved the AWS Industrial Software Competency in 2019.
Seeq’s advanced analytics application is a preferred solution for upstream production optimization in AWS Marketplace, enabling customers to rapidly investigate and share insights from process data stored on premise or in the cloud. Energy industry customers can also use Seeq to improve sustainability efforts, including carbon recapture, greenhouse gas detection and mitigation, and more.
Examples of use cases for energy customers using Seeq on AWS include one company deploying a real-time event detection model for analyzing well production performance across its asset base. A second company is reducing unplanned downtime and unifying data to optimize asset uptime by using Seeq to connect to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and its on-premises historic data.
Seeq on AWS can be procured in AWS Marketplace, which simplifies the procurement process and provides incentives for enterprise customers through the AWS Enterprise Discount Program. In addition, all AWS Marketplace sellers are verified as “ready-to-run” on AWS, expediting the purchase process. This streamlined approach to technology deployment enables companies using Seeq to quickly and easily realize the benefits of advanced analytics.
In addition to AWS data services, Seeq connects to an extensive set of data storage platforms from vendors including OSIsoft, Siemens, GE, Honeywell, Inductive Automation, AVEVA, AspenTech, Yokogawa, InfluxDB, Snowflake, and others. Seeq is available worldwide through a global partner network of system integrators, which provides training and resale support for Seeq in over 40 countries, in addition to its direct sales organization in North America and Europe.
To learn more about Seeq, visit www.Seeq.com
About Seeq
Founded in 2013, Seeq publishes software applications for manufacturing organizations to rapidly find and share insights. Oil & gas, pharmaceutical, specialty chemical, utility, renewable energy and numerous other vertical industries rely on Seeq to improve production outcomes, including yield, margins, quality, and safety. Headquartered in Seattle, Seeq is a privately held virtual company with employees across the United States and sales representation in Asia, Canada, Europe, and South America. To learn more about Seeq visit ww.seeq.com.
ABB launches industry-first smart factory solution for safer, more autonomous and efficient steel melt shop operations
Pioneering technology leader ABB has launched ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop, the first smart factory digital application of its kind for the metals industry. It is designed to increase melt shop productivity, save energy and improve employee safety, with payback within six months.
- ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop digitally connects all steel melt shop processes and moving equipment to synchronize operations and improve production efficiencies, moving steelmakers towards autonomous operations
- The new digital application automates and optimizes ladle and crane movements in steel melt shops enabling metals producers to closely track and schedule the transport of molten metal from furnace to caster
- The solution has already been installed by JSW Steel Ltd, India’s leading steel company
Based on advanced digital algorithms, the new solution is unique in that it offers not only powerful real-time ladle tracking but also automated crane scheduling and a predictive thermal modelling engine. The tracking engine follows ladle movement via cranes and transfer cars in real time. Radar and laser positioning technologies provide accurate visualization while reducing hardware footprint and maintenance needs compared to radio-frequency identification (RFID) solutions. The automated crane scheduling includes job forecasting, route planning and automatic acknowledgement of jobs.
This will enable steelmakers to move towards autonomous operations by eliminating manual co-ordinations, with increased safety in hot zones due to lower footfall.
The thermal engine function uses ladle thermal history from the tracking engine and forecasted heat movement from scheduling engines to predict the thermal loss during ladle transfer and predicts the correct lift temperature at ladle furnace. This results in better superheat compliance at the caster, eliminating caster slowdowns, hence increasing productivity.
Steelmakers can expect ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop to help increase superheat compliance to enable 4-5 percent higher casting speeds to improve productivity and reduce arcing by 5 degrees Celsius per heat in ladle furnaces for increased energy and cost efficiency.
 The solution results in better superheat compliance at the caster
The solution results in better superheat compliance at the caster
ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop has already been installed by JSW Steel Ltd, India’s leading steel company, where it has been integrated into a wider expansion at Dolvi Works plant in Maharashtra state. It is expected to increase the company’s EBITDA profit by around $2million per annum through 4 percent higher casting speeds, time savings of one working day per month and additional output equating to 24,000 tons a year.
“We’re proud to launch ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop – the first of its kind in the metals industry, enabling steelmakers to digitally connect all processes and moving equipment in the melt shop, achieving synchronized operations and removing bottlenecks in production capacity,” said Tarun Mathur, Global Product Manager, Metals Digital, ABB. “The digitalization of core processes will drive new levels of productivity, safety and sustainability outcomes for the metals sector.”
This application uses all standard communications protocols, employs ABB’s multi-layered defense-in-depth approach to cyber security and is compatible with both ABB and third-party systems.
Benefits of the new ABB Ability™ Smart Melt Shop include:
Productivity
- 4-5 percent increased casting speed due to better superheat compliance
- Reduced tapping delays, in EAF or converter due to more efficient scheduling of cranes for ladle movement
- Better ladle management and maintenance planning thanks to access to historical data on all movements
- Increased manpower productivity since no manual intervention or acknowledgement is required
Energy efficiency
- 5 degrees Celsius less arcing per heat (batch) in ladle furnace using thermal models to accurately predict target lift temperature
- Improved decision-making thanks to forecasting of ladle movements and crane schedules
Safety
- Increased safety with less footfall in hot zones which would otherwise be needed to manage ladle and crane movement
ABB (ABBN: SIX Swiss Ex) is a leading global technology company that energizes the transformation of society and industry to achieve a more productive, sustainable future. By connecting software to its electrification, robotics, automation and motion portfolio, ABB pushes the boundaries of technology to drive performance to new levels. With a history of excellence stretching back more than 130 years, ABB’s success is driven by about 105,000 talented employees in over 100 countries. www.abb.com
ABB’s Process Automation business is a leader in automation, electrification and digitalization for the process and hybrid industries. We serve our customers with a broad portfolio of products, systems, and end-to-end solutions, including our # 1 distributed control system, software, and lifecycle services, industry-specific products as well as measurement and analytics, marine and turbocharging offerings. As the global #2 in the market, we build on our deep domain expertise, diverse team and global footprint, and are dedicated to helping our customers increase competitiveness, improve their return on investment and run safe, smart, and sustainable operations. go.abb/processautomation
Revolutionary noise and vibration monitoring system, eNView, launches
KP Acoustics Group has launched eNView, a pioneering product that promises to disrupt the noise and vibration monitoring industry. Recently launched at London Build 2021, eNView is the award-winning, world-first system, which firmly places the power of acoustic measurement back into the hands of the user. Small, robust, reliable, and extremely smart, it facilitates real time, remote measurement, simple enough for anyone to understand.
Acoustics consultancy and environmental monitoring expert, KP Acoustics Group, has been clandestinely working on the system for years. The result is eNView, the user-friendly monitoring solution that combines real-time noise and vibration and dust monitoring equipment into one device, boasting plug and play usability. It’s also lightweight and compact, measuring just 95mm x 110mm x 225mm and weighing a mere 1.6kg. In a nutshell, it’s a system that’s so smart, you don’t have to be.
“It has been a year like no other for KP Acoustics Group,” explained Dr Kyriakos Papanagiotou, founder of KP Acoustics Group and the innovator behind eNView. “In June we became the only acoustics consultancy to offer our own research and development capability in-house and now we’re launching eNView — the paradigm shift in technology in environmental monitoring.
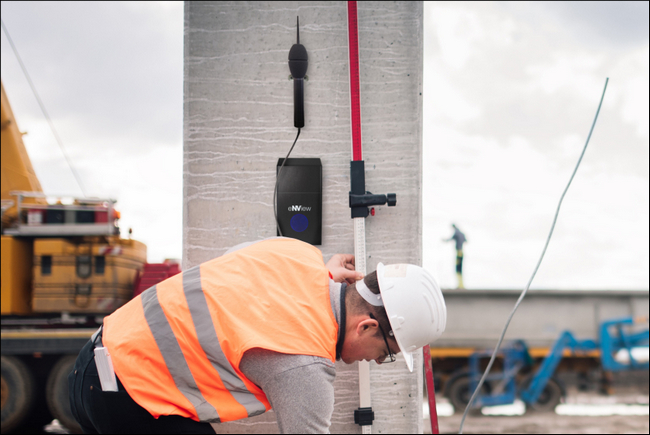

“We’re transforming the industry and London Build was the perfect environment for the much-anticipated launch. Construction, demolition, health and safety, highways and mining are just some of the sectors that eNView is perfect for.”
KP Acoustics Group exhibited from stand D59 at London Build 2021, where experts were on hand to offer product demonstrations and showcase eNView’s accompanying web application.
KP Acoustics Group was also showcasing its extended services offering in each of its three divisions: KP Acoustics, KP Monitoring and KP Acoustics Research Labs. The company recently expanded, continuing to offer its full range of acoustic consultancy services, alongside a separate division for environmental monitoring and its very own in-house research, development and education capability.
About KP Acoustics Group: KP Acoustics Group offers bespoke advice in acoustics, noise and vibration for a wide range of scenarios and industries across the world.
